Caring for Your Smile: Understanding Tooth Abscesses Stages and Their Treatment
A tooth abscess, also known as a dental or oral abscess, is a painful infection that can develop within a tooth, the jawbone, or the surrounding gums. Ignoring this infection, regardless of its location, could be better.
These abscesses do not resolve by themselves and can result in severe health issues if not treated. They don’t emerge suddenly but evolve through multiple stages before forming.
This article will dissect the stages of a tooth abscess and discuss its causes, symptoms, potential complications, and treatment options.
What is a Tooth Abscess?
A tooth Abscess is a condition where pockets of pus form due to a bacterial infection in the tooth, putting you at risk for a dental abscess.
Surprisingly, a tooth abscess is the body’s way of defending itself against infection. Containing the infection with pus prevents it from spreading to other areas. Gum or tooth abscesses are among the most common types, although abscesses can occur elsewhere in the body.
However, despite its defensive role, a dental abscess can harm teeth and gums, potentially eroding the periodontium—the tooth structure consisting of gum, periodontal ligament, and bone—and causing irreversible damage. Sometimes, removing the affected tooth is the only solution.
Tooth decay often triggers dental abscesses, which can also occur due to tooth fractures, cracks, or chips. Regardless of the cause, bacteria are primarily to blame as they infiltrate through cavities or tooth defects. While the body forms pus as a protective shield against bacterial invasion, it can ironically lead to more harm than good.
Types of Tooth Abscesses
Dental abscesses come in different types depending on their location within the mouth. They are as follows:
- Gingival Abscess – This type of abscess forms on the surface of the gum tissue, often resembling a small, visible pimple. Treatment and recovery from a gingival dental abscess are easy when detected early.
- Periodontal Tooth Abscess – This abscess occurs deeper within the gum, typically within gum pockets. Since the pus cannot quickly drain, a periodontal tooth abscess has the potential to spread to surrounding bone and tissue.
- Periapical Abscess – This Abscess can erode a tooth’s protective enamel and inner dentin. Once it penetrates the dentin, it can attack the soft inner pulp where the tooth’s nerves reside, causing severe pain. The primary solution for this type of Abscess is a root canal procedure to save the tooth.
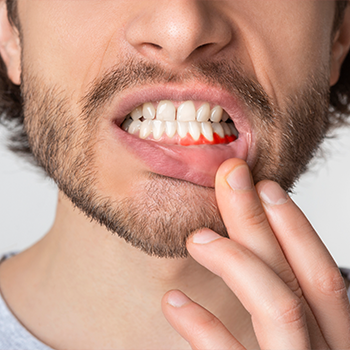
Tooth Abscess Stages
Many people aren’t aware of a tooth or gum infection until it reaches advanced stages. However, infections or abscesses don’t happen suddenly overnight. Understanding the progression of all the stages of an abscess can help prevent its development.
Enamel decay:
Before an abscess forms, there must be an infection. Plaque, a sticky white buildup containing bacteria, naturally resides in the mouth and can accumulate on teeth. You might feel a filmy plaque texture when you run your tongue over your teeth in the morning. Regular flossing and brushing remove plaque and prevent its buildup. If plaque isn’t removed, it can solidify into tartar, leading to enamel erosion and, eventually, cavity formation.
Dentin decay:
When cavities are left untreated, they worsen and lead to decay in the dentin. Bacteria continue their journey through the enamel and reach the softer layer beneath, called dentin.
Pulp decay:
Once bacteria penetrate the dentin, they attack the tooth’s inner pulp. The dental pulp consists of cells, blood vessels, and connective tissue. It’s the soft, jelly-like core containing nerves and blood vessels. Infection and inflammation of the pulp can lead to intense pain as the body’s immune system attempts to fight off the infection, setting the stage for abscess formation.
Abscess formation:
During this stage, the body’s immune system fights the infection, forming pus and an abscess. Throbbing pain and discomfort are common as the Abscess develops. Since a tooth abscess won’t heal on its own, immediate dental or medical attention is crucial. Over time, an untreated abscess can continue eroding the tooth and eventually cause tooth loss.
Signs and Symptoms of Abscess Tooth
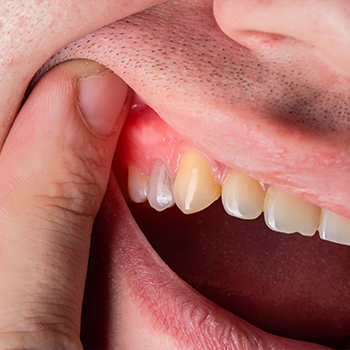
The typical symptom of a tooth abscess is pain. Many individuals describe the pain as intense and throbbing, often spreading towards the ear, jawbone, and neck.
Other symptoms of a dental abscess include:
- Sensitivity towards hot or cold foods and beverages
- A foul taste in the mouth
- Difficulty in swallowing or opening the mouth
- Insomnia or difficulty staying asleep.
If you notice any of the following symptoms, it could indicate that the tooth infection is spreading and requires immediate medical attention:
- Fever
- Vomiting
- Severe headache
- Nausea
- Double vision
Tooth Abscess Treatment
Dental infections, such as tooth abscesses, are treatable with proper care. You only need to seek medical attention quickly from a dentist or other healthcare professional. The location and severity of the dental abscess determine your doctor or dentist’s course of treatment.
Root Canal:
A root canal may be necessary for severe infections where the bacteria have reached the inner dental pulp. During the procedure, the dentist uses anesthesia to numb the tooth and the surrounding area. The infected pulp is removed, and space is filled to stop further infection. You may experience mild discomfort or pain for a few days afterward, but the anesthesia ensures you won’t feel pain during the root canal.
Tooth Extractions
Extraction may be the only option in cases where the tooth is badly damaged. This is usually considered a last resort. The dentist will use local anesthesia to numb the area before extracting the tooth. They will provide pain-relieving medications to manage any discomfort as you heal.
Antibiotics:
Sometimes, infections need antibiotics to kill the bacteria causing the problem. But just taking antibiotics might not be enough to fix it. Usually, they’re used together with a dental procedure to help clear up the infection better.
Do you have a tooth abscess or other dental problem that requires attention? Contact City of Lights Dental in Aurora, IL, to schedule an appointment. We will assess your dental concern and discuss treatment options. New patients can reach us at (630) 283-7694, and current patients can call us at (630) 283-7087.
FAQs
If you notice symptoms like fever, ongoing swelling, faster heartbeat, thirst, dehydration, or stomach pain, these could mean the infection is spreading. It’s important to get medical help right away.
Abscesses can form quite rapidly, sometimes within one or two days after you notice the first signs of infection. They can grow silently and without treatment for months or even years. Detecting them early is crucial, so we advise seeing a dentist for regular checkups. If you notice any signs of infection or trouble, don’t hesitate to contact us promptly.
You can decrease the risk of tooth abscess by regularly visiting your dentist for checkups and cleanings. Make sure you maintain good oral hygiene by brushing your teeth twice daily and flossing once a day at home.